Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
Geologists infer from the rounded, eroded shapes of the Appalachian Mountains
that
a. | the principle of uniformitarianism does not apply. | b. | the mountains formed
recently. | c. | the mountains are made of soft rock. | d. | the mountains have been eroding for millions of
years. |
|
|
|
2.
|
The most important factors in determining how fast a rock formation will
erode are
a. | carbon dioxide and acid rain. | b. | abrasion and acids from plant
roots. | c. | animal actions and oxygen. | d. | rock type weather, and
climate. |
|
|
|
3.
|
Decomposers are the soil organisms that
a. | store moisture in the soil. | b. | break down and digest the remains of dead
organisms. | c. | make spaces in the soil for air and water. | d. | burrow deep below
the topsoil. |
|
|
|
4.
|
What can cause the loss of soil that is not protected by plant cover?
a. | chemical weathering | b. | erosion by water or wind | c. | mechanical
weathering | d. | too many organisms in the soil |
|
|
|
5.
|
The process by which natural forces move weathered rock and soil from one place
to another is called
a. | soil conservation. | b. | deposition. | c. | abrasion. | d. | erosion. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Landslides mudflows, slump, and creep are all examples of
a. | mechanical weathering. | b. | runoff. | c. | mass
movement. | d. | soil formation. |
|
|
|
7.
|
Where a river flows from an area of harder rock to an area of softer rock, the
softer rock may wear away, eventually forming a drop called a(n)
a. | oxbow lake. | b. | gully. | c. | waterfall. | d. | delta. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Deltas are built up by
a. | deposition. | b. | leaching. | c. | abrasion. | d. | earthquakes |
|
|
|
9.
|
As more water flows through a river, its speed will
a. | stay the same. | b. | increase. | c. | decrease. | d. | reduce friction between the water and the
streambed. |
|
|
|
10.
|
How would a fast-flowing river be most likely to move sand-sized particles of
sediment?
a. | It would lift them and carry them downstream. | b. | It would dissolve
them completely in solution. | c. | It would roll or slide them along the
streambed. | d. | It would deposit them on the streambed. |
|
|
|
11.
|
What is the correct order (starting from the surface) of Earth’s
layers?
a. | crust, outer core, inner core, mantle | b. | mantle, outer core, inner core,
crust | c. | crust, mantle, outer core, inner core | d. | outer core, inner core, crust,
mantle |
|
|
|
12.
|
Earth’s mantle is
a. | a layer of molten metal. | b. | a layer of hot rock. | c. | a dense ball of
solid metal. | d. | a layer of rock that forms Earth’s outer skin. |
|
|
|
13.
|
Scientists think that convection currents flow in Earth’s
a. | continents. | b. | mantle. | c. | lithosphere. | d. | inner core. |
|
|
|
14.
|
Most geologists think that the movement of Earth’s plates is caused
by
a. | conduction. | b. | earthquakes. | c. | convection currents
in the mantle. | d. | Earth’s magnetic field. |
|
|
|
15.
|
The geological theory that states that pieces of Earth’s lithosphere
(crust) are in constant, slow motion is the theory of
a. | subduction. | b. | plate tectonics. | c. | deep-ocean
trenches. | d. | sea-floor spreading. |
|
|
|
16.
|
A place where two plates slip past each other horizontally, moving in opposite
directions, is known as a
a. | sliding or transverse boundary. | b. | spreading or diverging
boundary. | c. | colliding or converging boundary. | d. | rift valley or
plataeu |
|
|
|
17.
|
A rift valley forms at a
a. | colliding or converging plate boundary | b. | spreading or
diverging plate boundary. | c. | sliding or transversing
boundary. | d. | deep-ocean trench. |
|
|
|
18.
|
A collision between two pieces of continental crust at a colliding boundary
produces a
a. | mid-ocean ridge. | b. | deep-ocean trench. | c. | rift
valley. | d. | mountain range. |
|
|
|
19.
|
The place where two plates come together is known as a
a. | sliding boundary. | b. | spreading boundary. | c. | colliding or
converging boundary. | d. | rift valley. |
|
|
|
20.
|
Geologists know that wherever plate movement stores energy in the rock along
faults,
a. | earthquakes are not likely. | b. | earthquakes are likely. | c. | an earthquake is
occurring. | d. | an earthquake could never occur. |
|
|
|
21.
|
Which of the following is a biotic factor in the grassland
ecosystem?
a. | water | b. | sunlight | c. | soil | d. | grass |
|
|
|
22.
|
The nonliving parts of an ecosystem are called
a. | populations. | b. | organisms. | c. | biotic
factors. | d. | abiotic factors. |
|
|
|
23.
|
To carry out photosynthesis, algae and plants use the abiotic factors
sunlight, carbon dioxide, and
a. | soil. | b. | salt. | c. | water. | d. | bacteria. |
|
|
|
24.
|
In which process do producers (plants) use carbon from carbon dioxide to produce
sugars and other carbon-containing molecules?
a. | the nitrogen cycle | b. | photosynthesis | c. | precipitation | d. | the water cycle |
|
|
|
25.
|
What gas do producers(plants) release as a result of
photosynthesis?
a. | hydrogen | b. | nitrogen | c. | oxygen | d. | carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
26.
|
What is the elevation at the highest point of the zipline? 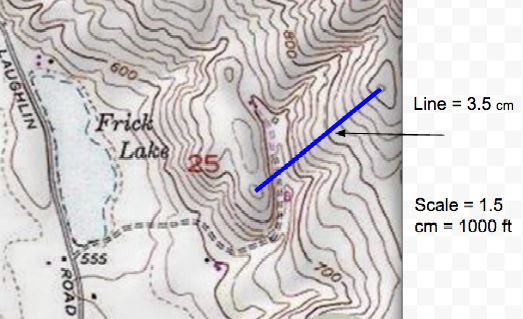 a. | 720 ft | c. | 920 ft | b. | 800ft | d. | 900 ft |
|
|
|
27.
|
What is the elevation of the lowest point of the zipline? 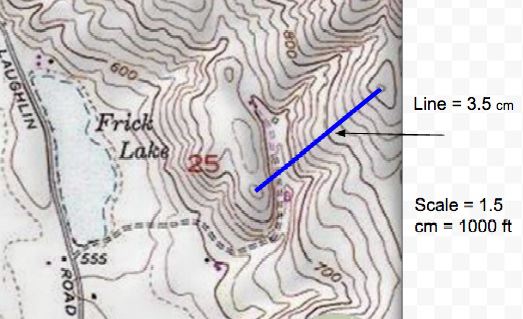 a. | 740 ft | c. | 700 ft | b. | 640 ft | d. | 600 ft |
|
|
|
28.
|
What is the total drop in elevation from the top of the zipline to the bottom of
the zipline? 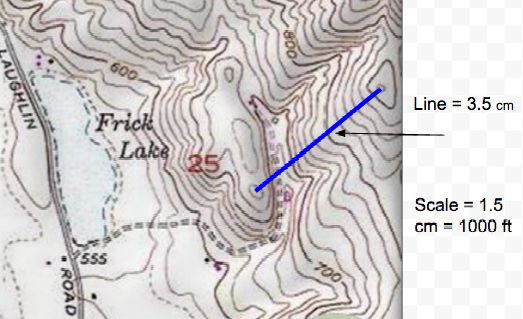 a. | 25 ft | c. | 180 ft | b. | 740 ft | d. | 100 ft |
|
|
|
29.
|
What is the horizontal distance of the zipline? 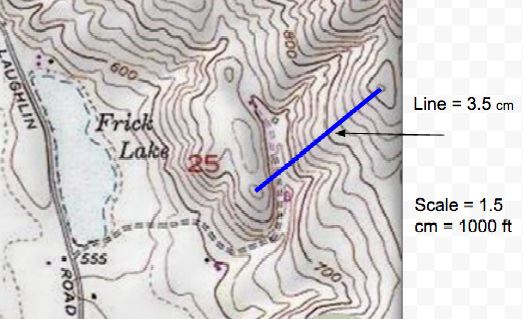 a. | 3533 ft | c. | 3500 ft | b. | 2333 ft | d. | 2500 ft |
|
Essay
|
|
|
30.
|
Explain how photosynthesis, respiration, food chains, and decomposers work
togethet to keep a closed ecosystem alive.
|